Modern financial systems generate more data than ever, but most of it arrives in unusable form. Think: raw CSV exports, endless transaction rows, and vague merchant names. For teams that need to assess financial health or automate decision-making, this kind of unstructured information creates more friction than clarity.
Smart data changes that.
It refers to financial information that’s cleaned, categorised, and ready to use. Instead of just listing transactions, it tells you what those transactions actually mean, from detecting salary patterns to flagging recurring subscriptions or identifying high-risk activity.
This blog explores what smart data really is, how it differs from traditional raw data, and why more financial platforms are building on top of intelligent data models to power automation, reduce errors, and improve customer outcomes.
What Is Smart Data?
At its core, smart data refers to financial information that’s been cleaned, categorised, and enriched to provide meaning, not just numbers.
Unlike raw data, which is often messy and hard to interpret, smart data is structured in a way that makes it immediately useful. For example, instead of showing a vague transaction from “XYZ LTD,” smart data might classify it as Groceries – Tesco – £42.00, tagged with merchant metadata, geolocation, and spending category.
It’s the difference between what happened and what it means.
Key Characteristics:
- Structured: Organised with consistent fields and standardised formats.
- Contextual: Each data point includes metadata like merchant, category, and channel (e.g. in-store, online).
- Usable: Ready for analysis, automation, and decision-making without manual cleanup.
Smart data is typically generated through enrichment layers that sit on top of raw transaction feeds. These layers apply rules, machine learning, or third-party intelligence to turn an unstructured bank feed into categorised, meaningful outputs tailored for finance teams, product developers, or compliance systems.
This transformation enables financial platforms to move beyond spreadsheets and start building products around real customer behaviour.
How Smart Data Works in Financial Platforms
Smart data doesn’t just appear; it’s created by transforming raw inputs into structured, meaningful information. Most financial platforms receive data from sources like bank feeds, credit files, or spending records. But on its own, that data is often incomplete, duplicated, or hard to interpret.
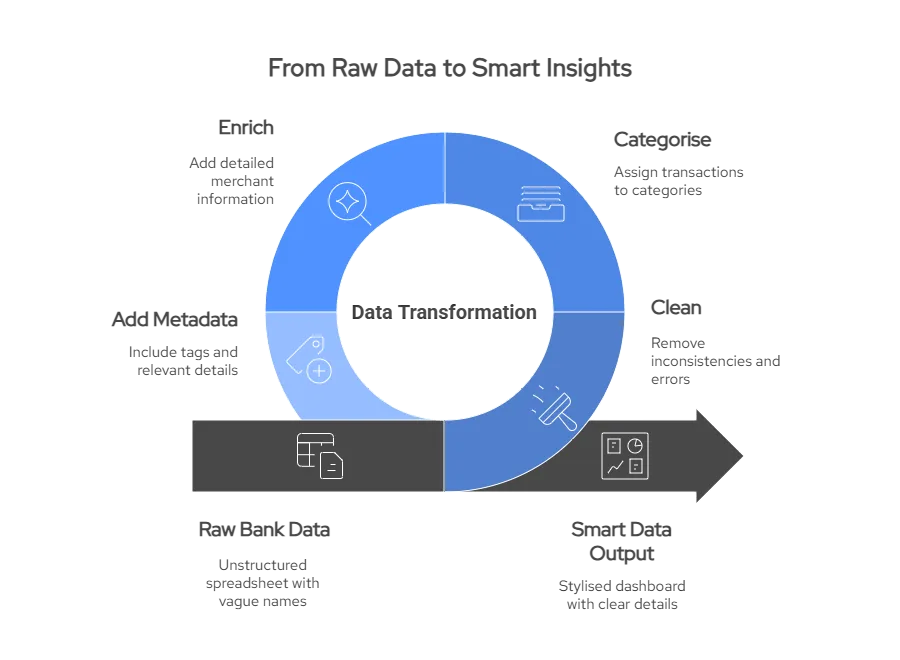
Here’s how the transformation works:
1. Ingestion
The system collects raw data, for example, transaction records from bank APIs or accounting software exports.
2. Cleaning & Deduplication
Inaccurate or duplicate entries are flagged and removed. This ensures only valid, unique data points are retained.
3. Categorisation
Transactions are classified into readable formats like Transport – Uber, Income – Salary, or Bills – Utilities. This is often powered by predefined logic, merchant databases, and machine learning models.
4. Enrichment
Additional insights are layered on, such as:
- Merchant name and type
- Location of purchase
- Payment channel (e.g. contactless, online)
- Risk flags (e.g. gambling, payday loan usage)
5. Output as Smart Data
The final product is a structured data feed that any system, from underwriting engines to dashboards, can immediately use.
Why This Matters
With enriched data, a finance team doesn’t just see that £600 left a client’s account. They see that it was a rent payment, made monthly, with consistent timing. That context allows for faster decisions, better user experiences, and automated reporting.
Smart data is what turns passive transaction logs into active insights.
Use Cases of Smart Data in Financial Services
Smart data isn’t just cleaner, it’s actionable. By turning vague bank feeds into categorised, readable insights, financial services can speed up decisions, reduce manual work, and personalise their offerings across different departments.
Here are some of the most valuable use cases:
✅ Lending: Faster, Smarter Affordability Checks
Instead of asking borrowers to upload payslips or bank statements, lenders can access enriched income and expense data. Categorised insights show:
- Regular income patterns (e.g. salary, benefits)
- Outgoings like rent, subscriptions, and high-risk spending
- Disposable income trends over time
This helps assess creditworthiness without friction or delay.
✅ Wealth Management: Real-Time Risk Profiles
Smart data helps investment platforms and advisors go beyond static questionnaires. By analysing client cash flow, spending stability, and savings behaviour, firms can:
- Tailor portfolios to actual financial behaviour
- Detect risk exposure early
- Improve investor segmentation
✅ Insurance: Claims & Policy Personalisation
Insurers can use transaction patterns to validate claims and build risk-aware policies:
- Detecting regular gym memberships or rideshare usage
- Verifying loss-of-income claims via bank activity
- Identifying potential fraud through behavioural anomalies
✅ Accounting: Auto-Categorisation for Reconciliation
For small businesses and accountants, enriched transaction feeds remove the need for manual tagging:
- Classify expenses automatically by type and VAT code
- Match payments with invoices for faster month-end close
- Detect duplicates or irregularities instantly
✅ Payments & Budgeting Apps: Real-Time Insights
Consumer-facing apps use smart data to:
- Show real-time spending insights by category
- Nudge users on saving opportunities or overspending
- Offer contextualised payment suggestions
What’s the difference between smart data and enriched data?
Smart data refers to the final output, categorised, usable financial information. Enrichment is the process that adds context to raw data, making it smart. So, enrichment is one step toward generating smart data.
Can small teams or startups use smart data without building complex systems?
Yes. Many API providers, including Finexer, offer ready-to-use categorised transaction data, so you don’t need to invest in internal data science or infrastructure.
Why Smart Data Is Becoming a Financial Staple
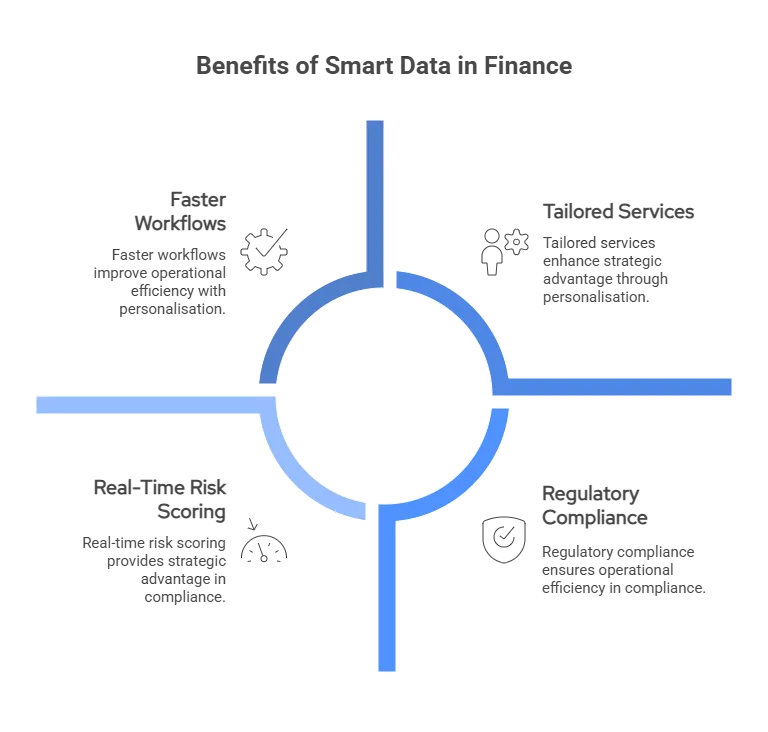
Smart data has quietly become the foundation for modern financial workflows. As customer expectations shift toward real-time decisions and personalised services, the need for clean, contextual, and instantly usable financial data is no longer optional; it’s expected.
Here’s why adoption is growing fast across fintech and financial services:
1. Real-Time Decision-Making
Lenders, insurers, and platforms need to respond in seconds, not days. Structured financial data makes instant affordability checks, risk scoring, and fraud detection possible, without waiting for uploads or paperwork.
2. Smarter Personalisation
Categorised insights help businesses tailor offerings based on real behaviour, not assumptions. Whether it’s suggesting a better savings plan or flagging unusual spending, users get value that feels relevant and timely.
3. Lower Operational Overhead
By reducing manual data cleaning, tagging, and matching, smart data saves teams time and reduces human error. Finance and ops teams can focus on higher-value tasks like analysis, forecasting, or client advisory.
4. Compliance Without Friction
When financial data is enriched and labelled properly, it becomes easier to meet reporting, affordability, and transparency requirements, all while keeping the user journey smooth.
In short, structured intelligence from transaction feeds is powering everything from onboarding flows to financial planning tools. It’s not just about access to data anymore; it’s about making that data work harder, smarter, and faster.
How Finexer Helps You Work with Smart Data
Smart data only becomes useful when it’s accessible, accurate, and easy to integrate, and that’s exactly what Finexer enables.
Through Finexer’s real-time bank data APIs, you can pull clean, categorised transaction data directly from 99% of UK banks, enriched with metadata to make every entry clear and usable from day one.
What you get with Finexer:
- ✅ Categorised bank feeds: Every transaction is enriched with merchant name, category, channel, and location
- ✅ Clean, ready-to-use outputs: No post-processing required, ideal for lending, accounting, wealthtech, or insurance workflows
- ✅ FCA-regulated infrastructure: Built for secure, consent-driven data access
- ✅ Developer-first experience: Fast integration, clear documentation, and full white-label support
Whether you’re building affordability checks, auto-reconciliation tools, or personalised dashboards, Finexer’s API gives your team the enriched insights needed to deliver faster and smarter financial experiences without the engineering burden of building enrichment layers from scratch.
Get Started
Connect today and see why businesses trust Finexer for secure, compliant, and tailored open banking solutions.
Try NowHow is smart data generated from bank feeds?
Smart data is generated through a series of steps: data ingestion, cleaning, categorisation, and enrichment. These steps transform raw bank feeds into structured, actionable formats ready for automation or analysis.
Is smart data secure and compliant with financial regulations?
Yes. When accessed through regulated providers, smart data is collected with user consent and handled under FCA and PSD2 guidelines, ensuring full compliance and security.
What are the real benefits of using smart data for financial products?
Smart data helps reduce manual work, improves decision speed, enhances user personalisation, and makes it easier to meet compliance needs, all while delivering a better customer experience.
Finexer’s API delivers real-time bank data from 99% of UK banks, with full developer support and zero setup fees.
